cf中的一个数学题
round 754
C
一开始我知道我写完肯定会T,但是还是写了下去,然而WA7,我想怎么会不是T呢,T了才有改进的动力啊。
第二天的中午才发现了问题,原来由于数的乘积非常的大,因此仅仅一次的取正是不行的。
num = (num+mod)%mod;变成了num = (num+mod*n)%mod;
然后当然就理所当然的T了。
对等式进行相应的化简
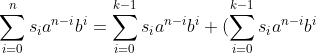·(a^{-k}b^k)+\dots+(\sum_{i=0}^{k-1}s_ia^{n-i}b^i)(a^{-k\frac{n+1}{k}-1}b^{k\frac{n+1}{k}-1})\\&space;=&space;\sum_{i=0}^{k-1}s_ia^{n-i}b^i(1+a^{-k}b^k+a^{-2k}b^{2k}+\dots&space;+&space;a^{-k\frac{n+1}{k}-1}b^{k\frac{n+1}{k}-1})\\&space;=&space;\sum_{i=0}^{k-1}s_ia^{n-i}b^i*(\frac{1-(a^{-k}b^k)^{\frac{n+1}{k}}}{1-(a^{-k}b^k)}))
前面一部分用快速幂,因为1e9+9是质数,任意数对该数的逆元必定存在。后面的部分用逆元来搞就行了
AC代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62
| #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const ll mod = 1e9+9; ll pow_mod(ll a, ll b){ ll ans = 1ll; while(b){ if(b&1){ ans=(ans*a)%mod; } a = a*a%mod; b>>=1; } return ans; } void extgcd(ll a,ll b,ll& d,ll& x,ll& y){ if(!b){ d=a; x=1; y=0;} else{ extgcd(b,a%b,d,y,x); y-=x*(a/b); } } ll inverse(ll a,ll n){ ll d,x,y; extgcd(a,n,d,x,y); return d==1?(x+n)%n:-1; } ll n ,a, b, k; string op; int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false); while(cin>>n>>a>>b>>k){ cin>>op; ll ans = 0; for(int i=0; i<k; i++){ ll num = 0; char temp = op[i]; if(temp == '-'){ num = (-1ll)*pow_mod(a, n-i)*pow_mod(b, i)%mod; num = (num+mod*n)%mod; } else{ num = pow_mod(a, n-i)*pow_mod(b, i)%mod; num = (num+mod*n)%mod; } ans = (ans+num+mod)%mod; } ll q = (pow_mod(a, (mod-2)*k)*pow_mod(b, k))%mod; if(q == 1){ cout<<ans*(n+1)/k%mod<<endl; } else{ ll inverse_deno = inverse((q-1), mod); cout<<((ans*(pow_mod(q, (n+1)/k)-1ll)%mod)*inverse_deno%mod+n*mod)%mod<<endl; } } return 0; }
|
D
一个思考题,第一眼看上去感觉在删边的时候要不断的维护删除的信息,感觉不可做。
但是看了别人的题解之后,发现删除的时候并不不需要维护。从底向上不断的删除就行了
题解
首先。若节点是偶数个,那么肯定不存在解,因为总共有奇数条边,每次删除偶数条边,最后不可能删完的。
d[i]: 表示的是i及i的子树中节点的总个数。
我们都是从d[i]为奇数的节点开始删除的,d[i]为奇数表示这个子树有偶数条边。因为从下往上删除,一定是符合要求的。
感觉这种不需要维护删除信息的思想非常的重要,把原来复杂的问题简单化。
还有,关同步大法好!!!!
AC代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64
| #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int maxn = 2e5+10; vector<int> num[maxn]; int d[maxn]; int n; void dfs(int u, int fa){ d[u] = 1; for(int i=0; i<num[u].size(); i++){ if(num[u][i] == fa) continue; else{ dfs(num[u][i], u); d[u] += d[num[u][i]]; } } } void solve(int u, int fa){ for(int i=0; i<num[u].size(); i++){ int v = num[u][i]; if(v == fa) continue; else{ if(d[v]%2==0){ solve(v, u); } } } cout<<u<<endl; for(int i=0; i<num[u].size(); i++){ int v = num[u][i]; if(v == fa) continue; else{ if(d[v]%2==1){ solve(v, u); } } } } int main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(false); while(cin>>n){ int rt; if(n%2==0){ int temp; for(int i=0; i<n; i++) cin>>temp; cout<<"NO"<<endl; } else{ cout<<"YES"<<endl; for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){ int temp; cin>>temp; if(temp == 0) rt = i; num[temp].push_back(i); } dfs(rt, -1); solve(rt, -1); } } return 0; }
|
未解决的问题